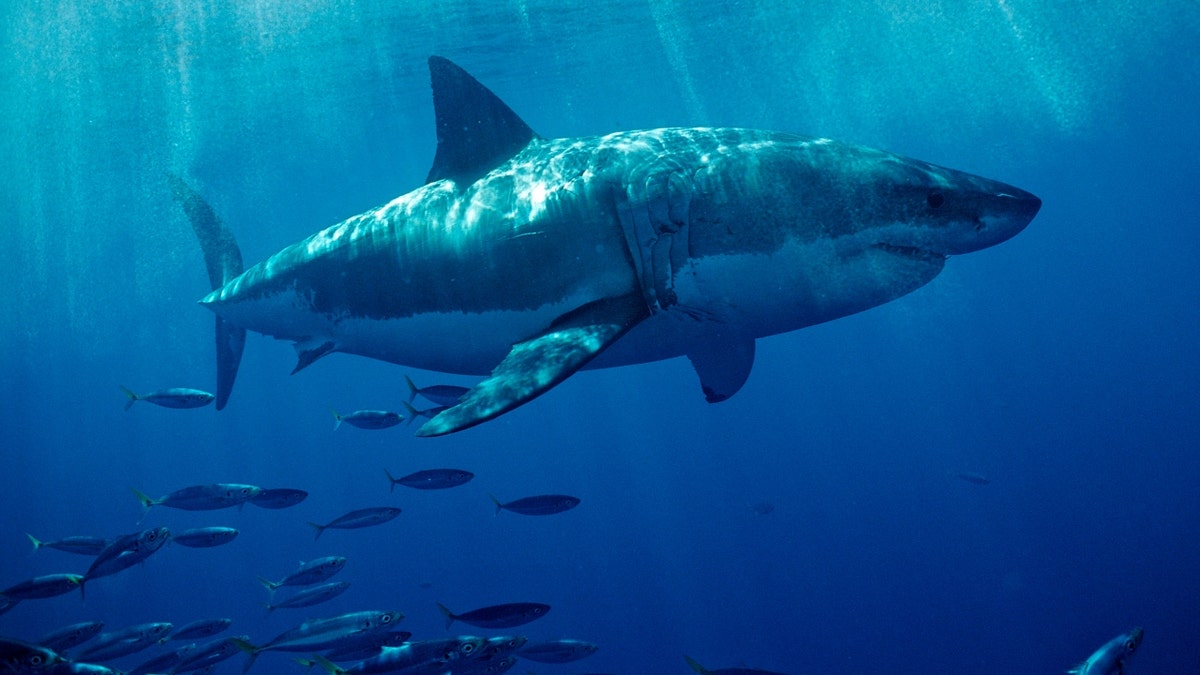
Great White Shark Attack: Understanding The Facts And Myths
Great white shark attacks are among the most captivating yet misunderstood phenomena in marine biology. These apex predators, known scientifically as Carcharodon carcharias, have captured the imagination of millions through movies and documentaries. Despite their reputation, great white sharks rarely target humans. Understanding their behavior, habitat, and the reasons behind these attacks can help dispel myths and promote coexistence.
When we hear about a great white shark attack, our minds often jump to fear and danger. However, these incidents are incredibly rare and often misunderstood. In reality, great white sharks play a vital role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. Their presence indicates a healthy ocean environment, as they prey on sick or weak animals, preventing the spread of disease.
As we delve deeper into this topic, we will explore the facts behind great white shark attacks, their behavior, and what you can do to stay safe in the water. This article will also touch on the importance of conservation efforts to protect these magnificent creatures. Let’s start by examining the key aspects of great white shark attacks and why they occur.
Read also:Nathan Fillion Kids A Complete Guide To His Family Life
Table of Contents
- The Biology of Great White Sharks
- Great White Shark Attack Statistics
- What Causes Great White Shark Attacks?
- Types of Great White Shark Attacks
- Staying Safe from Great White Shark Attacks
- Common Myths About Great White Shark Attacks
- The Importance of Great White Shark Conservation
- Where Do Great White Shark Attacks Occur?
- Scientific Research on Great White Sharks
- Conclusion: Coexisting with Great White Sharks
The Biology of Great White Sharks
Great white sharks are one of the most fascinating creatures in the ocean. They belong to the family Lamnidae and are known for their powerful bodies, sharp teeth, and incredible speed. These sharks can grow up to 20 feet in length and weigh over 4,000 pounds. Their streamlined shape allows them to swim at speeds of up to 35 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest predators in the sea.
Key Characteristics of Great White Sharks
- Powerful jaws with serrated teeth designed for cutting through flesh
- Keen sense of smell, capable of detecting blood from miles away
- Electroreception, allowing them to sense electrical impulses from prey
- Counter-shading coloration for camouflage in the water
Despite their fearsome reputation, great white sharks are not mindless killers. They play a critical role in the marine ecosystem by controlling populations of seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals.
Great White Shark Attack Statistics
Statistics show that great white shark attacks are incredibly rare. According to the International Shark Attack File (ISAF), there are only about 70-100 unprovoked shark attacks worldwide each year. Of these, only a small percentage involve great white sharks. In fact, humans pose a much greater threat to sharks than they do to us.
Annual Shark Attack Data
- Average of 5-6 fatalities globally per year
- Most attacks occur in shallow waters near the coast
- Surfers and swimmers are the most common victims
These statistics highlight the importance of education and awareness when it comes to shark encounters. By understanding the risks and taking precautions, we can significantly reduce the likelihood of an attack.
What Causes Great White Shark Attacks?
Great white shark attacks are usually the result of mistaken identity or curiosity. These sharks often mistake humans for their natural prey, such as seals or sea lions, especially when viewed from below against the surface of the water. Additionally, great whites are known for their "test bite" behavior, where they bite an object to determine what it is.
Common Factors Leading to Attacks
- Swimming in areas with high shark activity
- Wearing shiny jewelry or bright clothing that resembles fish scales
- Splashing excessively in the water
While these factors increase the chances of an encounter, it is important to remember that great white sharks are not naturally aggressive toward humans. Most attacks are accidental and occur when the shark feels threatened or confused.
Read also:Bambi Suwayji A Comprehensive Guide To Her Life Achievements And Legacy
Types of Great White Shark Attacks
Great white shark attacks can be categorized into three main types: hit-and-run, bump-and-bite, and sneak attacks. Each type reflects the shark's behavior and motivation during the encounter.
Hit-and-Run Attacks
These are the most common type of attack and typically involve a single bite. The shark quickly retreats after realizing the victim is not its usual prey. Hit-and-run attacks are usually not fatal and occur in shallow waters.
Bump-and-Bite Attacks
In bump-and-bite attacks, the shark circles the victim and bumps into them before biting. This behavior is often observed when the shark feels threatened or curious. Bump-and-bite attacks can be more serious, as the shark may bite multiple times.
Sneak Attacks
Sneak attacks occur without warning and are often fatal. These attacks are rare and usually happen in deep waters where great whites hunt their natural prey. Sneak attacks are often associated with larger sharks and may involve multiple victims.
Staying Safe from Great White Shark Attacks
While great white shark attacks are rare, it is important to take precautions when swimming or surfing in areas known for shark activity. Here are some tips to help you stay safe:
- Avoid swimming at dawn or dusk, when sharks are most active
- Stay close to shore and avoid swimming alone
- Do not wear shiny jewelry or brightly colored clothing
- Be aware of your surroundings and look for signs of shark activity
By following these guidelines, you can minimize the risk of encountering a great white shark and ensure a safe and enjoyable experience in the water.
Common Myths About Great White Shark Attacks
There are many myths surrounding great white shark attacks, often perpetuated by movies and media. Here are some of the most common myths and the truth behind them:
Myth: Great White Sharks Are Man-Eaters
Fact: Great white sharks do not intentionally hunt humans. Most attacks are accidental and occur when the shark mistakes a human for its natural prey.
Myth: Sharks Can Smell Blood from Miles Away
Fact: While great white sharks have an excellent sense of smell, they cannot detect blood from miles away. Their ability to sense blood diminishes with distance and water currents.
Myth: Sharks Attack Because They Are Hungry
Fact: Great white sharks are not motivated by hunger when they attack humans. Most attacks are the result of curiosity or mistaken identity.
The Importance of Great White Shark Conservation
Great white sharks are a vital part of the marine ecosystem and play a crucial role in maintaining balance in the ocean. However, these magnificent creatures face numerous threats, including overfishing, habitat loss, and climate change. Conservation efforts are essential to ensure their survival and protect the health of our oceans.
Conservation Strategies
- Establishing marine protected areas to safeguard shark habitats
- Implementing fishing regulations to reduce bycatch
- Raising public awareness about the importance of sharks
By supporting conservation initiatives and promoting responsible tourism, we can help protect great white sharks and preserve their place in the marine ecosystem.
Where Do Great White Shark Attacks Occur?
Great white shark attacks are most commonly reported in areas with high populations of seals and sea lions, such as the waters off California, South Africa, and Australia. These regions provide an abundant food source for great whites and attract large numbers of sharks during certain times of the year.
Hotspots for Great White Shark Encounters
- Guadalupe Island, Mexico
- Farallon Islands, California
- Gansbaai, South Africa
While these areas are known for shark activity, it is important to remember that attacks remain rare and are often avoidable with proper precautions.
Scientific Research on Great White Sharks
Scientists are continually studying great white sharks to better understand their behavior, migration patterns, and ecological role. Advances in technology, such as satellite tagging and DNA analysis, have provided valuable insights into the lives of these elusive creatures.
Key Findings from Recent Studies
- Great white sharks migrate long distances, often crossing entire ocean basins
- Sharks have complex social structures and exhibit cooperative behavior
- Climate change may impact shark populations by altering prey distribution
Continued research is essential to inform conservation efforts and address the challenges facing great white sharks today.
Conclusion: Coexisting with Great White Sharks
In conclusion, great white shark attacks are rare and often misunderstood. By educating ourselves about these incredible creatures and taking precautions in the water, we can reduce the likelihood of an encounter and promote coexistence. Great white sharks play a vital role in maintaining the health of our oceans, and it is our responsibility to protect them for future generations.
We encourage you to share this article with others and continue learning about great white sharks. For more information on marine conservation and shark safety, explore the resources available on our website. Together, we can make a difference in protecting these magnificent creatures and preserving the beauty of our oceans.